Log In
Sign Up
Deloitte Interview Q & A
Deloitte 50+ most Asked Technical Questions
Question 1:
Do you have any technical certifications?
Explanation:
- If you have listed certifications in your resume, the interviewer will ask this question.
- Describe the certifications in detail, including your training, projects, seminars, webinars etc.
- List only those certifications that are relevant to the job. And co-relate how your certification can help in the job.
Question 2:
What is the extent of your technical expertise?
Explanation:
- You have to rate your technical skills.
- The interviewer wants to check how in touch you are with the current technologies.
- Mention the technologies you have worked with, and how good you are with them.
- Additionally mentioning technologies like ML, AL, AWS etc which are the most sought after technologies right now will earn you more points.
- However do not lie, cause they will cross check your answers.
Question 3:
What do you do to improve your technical skills?
Explanation:
- An employee who is always striving to better themselves, is a valuable asset.
- The interviewer wants to know how you have tried to better yourself and skills.
Mention methods like :-
- Reading technical books and journals. (mention the names of a few)
- Attend online webinars and tutorials regarding the skills.
- Build a git-hub profile(show your projects to the interviewer)
- Learning new tools
Question 4:
Give an example of how you apply your technical knowledge in a practical way?
Explanation:
- This is a behavioral interview type question.
- You can follow the STAR method to answer questions of this type.
- Follow the framework and explain how you have applied your technical skills in any project or product. How you did it and what were the results.
Question 5:
What was the recent technical project you worked on? What were your key responsibilities?
Explanation:
- This is a behavioral interview type question.
- If you have worked on a project that used the same technologies that were mentioned in the job description/eligibility criteria, try to mention that.
- Else you can mention any other project.
- Use the STAR method to answer questions of this type.
- If the interviewer has mentioned a specific part like your responsibilities, or the challenges you faced, describe that part with more emphasis.
Question 6:
What is the production deployment process you follow?
Explanation:
- Deployment is the step by step process of making an application ready.
- It varies from individual to individual and organization to organization.
- Some of the common models are Waterfall Model, Iterative Model, Agile Model etc.
- You can follow one of these, or if you have your own mix you can talk about that.
- Explain your thought process to the interviewer.
Question 7:
What do you like most about the IT industry? What do you enjoy the least about it?
Explanation:
- Mention the features of IT that you like.
- For instance you can mention that being able to work with emerging technologies is your favorite feature.
- Also mention the aspects that you wish would change.
Question 8:
Why is a solution design document important?
Explanation:
- Solution design document is a document on which the details of a project are written before its implementation.
- It’s an important document to communicate the technical details of the plan to a team.
- It also helps organize one’s thoughts before you start working on the project.
Question 9:
Whenever you solve a problem, who do you keep in mind? The end-user, the business, or yourself, and why?
Explanation:
- The aim of any product is to be of service to someone.
- It could be the user, the company or the creator.
- Mention who you think is the one of service.
- Explain who is the main benefactor for the product developed by you.
Question 10:
How many programming languages do you know?
Explanation:
- Whatever languages you have mentioned in your resume, tell them here.
- Sometimes interviewers will ask you to rate yourselves, in the languages you mentioned.
- Do not rank yourself very high like a 9, because they might ask you advanced level questions which if you are unable to answer will create a negative impression.
- Whichever language you rate yourself highest in the follow up questions will be mostly from there only.
- They will also ask questions as to why you prefer that language in particular or why you are stronger there.
Question 11:
What is the use of printf() and scanf() functions?
Explanation:
- printf() function displays integer, character, float or string values on the screen.
- %d-displays an integer value
- %s-displays a string
- %c-displays a character value
- %f-displays a floating value.
- scanf() function takes input from the user.
Question 12:
What is the static variable? What is its use?
Explanation:
A variable which is declared static, is known as a static variable. These variables are able to retain its value between multiple function calls.
Syntax:
static int y=10;//static variable
Static variables are used because these variables can be accessed from anywhere in the program.
Static variables are used as common values and are shared by all the methods.
Question 13:
What is the difference between call by value and call by reference in C?
Explanation:
Question 14:
What is Recursion in C?
Explanation:
Recursion is the process where a function calls itself. This function is known as a recursive function. There are 2 phases of recursion:-
- Winding phase – when a recursive function calls itself, this phase reaches its end when the condition is fulfilled.
- Unwinding phase – when the condition is fulfilled, this phase starts and the control is returned to the original call.
Question 15:
What is a pointer in C? What are its uses?
Explanation:
A pointer is a variable referring to the address of a value. When a variable is declared inside a program, the system allocates some memory to it. This memory contains an address number. The variables that hold this address number are called pointer variables.
Syntax: Data_type *p;
P is a pointer variable holding the address number of data_type value.
Uses of Pointer:-
Pointers are used in accessing elements through an array. Pointers are used to pass a reference of a variable to another function.
Question 16:
What is a NULL pointer and far pointer?
Explanation:
- Null Pointer – Null pointer is a pointer that does not refer to any address of value but to NULL. When “0” is assigned to a pointer of any type, it creates a Null pointer.
- Far Pointer – A far pointer is a pointer that can access all the 16 segments, i.e. the whole residence memory of the RAM. It is a 32 bit pointer that obtains information from outside the memory in a given section.
Question 17:
What is a dangling pointer? How is it overcome?
Explanation:
Dangling pointer is a problem that arises when an object is deleted without modifying the value of the pointer. Thus the pointer is now pointing to a deallocated memory.
In other words, if a pointer say A is pointing to a memory location, but another pointer B deletes the memory occupied by A while A is still pointing to that location, A becomes a dangling pointer.
- The problem is overcome by assigning a NULL value to the dangling pointer.
- After de-allocating the memory from a pointer variable, the pointer is assigned to a NULL value.
- Thus the pointer is not pointing to any memory location, therefore it’s no longer a dangling pointer.
Question 18:
What is an infinite loop?
Explanation:
A loop running continuously for an indefinite number of times is called the infinite loop.
Question 19:
What is a command line argument?
Explanation:
The argument passed to the main() function while executing the program is known as a command line argument.
Question 20:
Can we compile a program without the main() function?
Explanation:
We can compile a program without the main() function, however the program won’t be executed. However adding #define, we can compile and run the program without using the main() function.
Question 21:
What is an object and class?
Explanation:
- Object – It is a collection of methods and classes which represent its state and execute operations.
- Class – It is used to define new types of data which is then used to create objects.
Question 22:
What do you mean by JVM, JDK and JRE?
Explanation:
- JVM – Java Virtual Machine. Offers runtime environment for cods to be executed.
- JRE – Java Runtime Environment. It’s the collection of files that are needed during runtime by JVM.
- JDK – Java Development Kit. It is a kit which contains the tools necessary to write and execute a program.
Question 23:
How can you restrict inheritance?
Explanation:
By the following methods:
- Using the final keyword.
- Making the method final.
- Using private constructor.
- Using (//) Javadoc comment
Question 24:
What are static methods and static variables?
Explanation:
They are methods and variables shared by all the objects in a class. Their static nature comes from the class and not from the object itself.
Question 25:
What is enumeration?
Explanation:
It is an interface you can use to access original data structure.
Question 26:
What is the use of ‘this’ keyword in JAVA?
Explanation:
‘this’ keyword is used to refer to a current object, to invoke the current class method or class constructor.
It is also used to pass on as an argument into methods or constructors.
Question 27:
What is the final variable?
Explanation:
In Java, the final variable is used to restrict the users from updating the variable. The final variable once assigned can not be changed after that.
Question 28:
Why is JAVA platform independent?
Explanation:
Java is platform independent because of its byte codes which can run on any system regardless of its operating systems.
Question 29:
What are access modifiers in Java?
Explanation:
Access modifiers are special keywords that can restrict the access of a class, constructor, data member and method in another class. They are of 4 types:-
- Default
- Private
- Protected
- Public.
Question 30:
What is method overloading?
Explanation:
It is a polymorphism technique that allows us to create multiple methods with the same name but different signatures.
Question 31:
What is interpreted language?
Explanation:
An interpreted language executes its statements line by line. Interpreted language codes can run directly from the source code with no intermediary compilation step.
Question 32:
What are lists and tuples?
Explanation:
Lists and tuples are sequence data types. The objects stored in both the sequences can have different data types.
- List are represented by square brackets [“”,’’]
- Tuples are represented by round brackets (“”,””)
- The difference between the two is that lists are mutable while tuples are immutable. Which means that lists can be modified while tuples can not be modified.
Question 33:
What is pass in Python?
Explanation:
Pass keyword represents a null operation in python. Used for the purpose of filling up empty block code which may execute during runtime, but are yet to be written
Question 34:
What is self in Python?
Explanation:
Self is a keyword that defines an instance of an object of a class. It is explicitly used as the first parameter.
Question 35:
What is slicing in Python?
Explanation:
Slicing is used to break up a list or tuple.
- Start: it is the starting index from where the list is sliced
- Stop: It is the ending index where the list is stop
- Step: It is the number of steps to jump
Syntax:
[start:stop:step]
Question 36:
What is the use of break statement?
Explanation:
- It is used to terminate the execution of the current loop.
- Break statement, breaks the current execution and transfer control to outside the current block.
Question 37:
What is an operator in Python?
Explanation:
Operator is a symbol, which is used on some values and produces an output as a result. Operator works on operands.
Operators are of unary, binary or ternary types depending on the number of operands required.
They include:-
- Arithmetic
- Relational
- Assignment
- Logical
- Identify
- Bitwise
Question 38:
What is swapcase() function in Python?
Explanation:
- It is a string function which converts all uppercase characters into lowercase and vice versa.
- It is used for altering the existing case of the string.
- This method creates a copy of the string which contains all the characters in the swap case.
Question 39:
What is the Python decorator?
Explanation:
It is a powerful tool that allows you to add functionality in an existing code. It is also known as meta-programming.
Question 40:
What is the difference between Python Arrays and lists?
Explanation:
Question 41:
What is DBMS?
Explanation:
DBMS stands for Database Management System. It carries out operations like creation, maintenance and use of a database.
Question 42:
What are tables, fields and record?
Explanation:
- Tables: Data organized in a model with Rows and Columns is called a table. Rows are horizontal while tables are vertical.
- Fields: In a table there are a specified number of columns known as fields.
- Records: There are infinite number of rows which is called a record.
Question 43:
What is Foreign Key?
Explanation:
Foreign Key is a key which links 2 tables.
It is a field or a collection of fields in a table that corresponds to the Primary Key of another table.
Question 44:
What is the difference between DELETE and TRUNCATE?
Explanation:
Question 45:
What is a constraint?
Explanation:
Constraints are limitations on the data type of a given table. Samples of constraints are:
- Not Null
- Check
- Default
Question 46:
What is ACID property in a database?
Explanation:
- Atomicity – It states each transaction is all or nothing. If one part of the transaction fails, the entire transaction fails.
- Consistency – It states that data must follow all validation rules. A transaction never leaves the database without being completed.
- Isolation – Isolation provides concurrency control. It ensures that concurrent property of execution should not be met.
- Durability – Once a transaction is committed it will remain committed regardless of the situation, power loss, crashes etc.
Question 47:
What is SQL?
Explanation:
SQL stands for Structured Query Language and is used to communicate with the Database. It is a standard language for accessing and manipulating databases.
Question 48:
What is a unique key?
Explanation:
- A Unique key constraint identifies each record in the database. It provides for the column or set of columns.
- A unique key is a set of one or more than one field of a table that can uniquely identify a record in a database table.
Question 49:
What is a relationship and what are they?
Explanation:
Relationship is the interconnection of tables within the database. There are various relationships,
- One to One Relationship.
- One to Many Relationship.
- Many to One Relationship.
- Self-Referencing Relationship.
Question 50:
What is a query?
Explanation:
A query is really a request for data. A DB query is a code written in order to get the information back from the database. You ask the database for something and it answers in the best way it knows with data as a result of a query.
Question 51:
What is Machine Learning?
Explanation:
Machine Learning is the science of getting computers to act in a real-time situation without being programmed explicitly. It is an application of AI and it enables systems to learn automatically and to improve from previous experience.
Question 52:
What is Supervised, Unsupervised and Semi-Supervised learning?
Explanation:
- Supervised learning – The model is trained on labeled data, and then it predicts based on the labeled data, Therefore it requires a supervisor to train the data.
- Unsupervised learning – The model is trained on unlabeled data. The model tries to find patterns and relationships in the data and classify them accordingly.
- Semi-Supervised Learning – It uses some amount of labeled data and a large amount of unlabeled data. The goal is to classify unlabeled data with the help of labeled data.
Question 53:
What are training set and test set in Machine Learning and why are they important?
Explanation:
- Training set is a set given to the model for training, analyzing and learning.
- Test set is a set used for testing the model locally before using it in a real time application.
Question 54:
Explain the stages of building a Machine Learning model.
Explanation:
- Data Collection: Appropriate data is collected using either some algorithm or manually.
- Data Processing: The collected data is processed by handling all the null values, categories etc.
- Model Building: The algorithms to create the model is decided and built.
- Model Evaluation: The model is evaluated using techniques such as accuracy score, z score etc.
- Model Saving and Testing: The model is saved for future use and real time testing is done.
Question 55:
How does IoT work?
Explanation:
Iot is built on the concept of AI. An IoT device has a sensor which collects data, the cloud facilitates the network between the devices, the software processes and stores the data and finally the UI enables the device to respond to the stimulation.
Question 56:
What is Natural Language Processing?
Explanation:
Natural language processing is a branch of Artificial Intelligence that deals with the conversion of Human Language to Machine Understandable language, so it can be processed by Machine Learning models.
Question 57:
What is IIOT?
Explanation:
IIOT(Industrial Internet of Things) are large scale IoT structures or systems that are used at the industrial level.
Question 58:
What is Deep Learning?
Explanation:
Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning. It is a neural network with multiple layers, which creates a stimulation of the human brain, allowing the model to lean from large amounts of data.
Question 59:
What is Arduino?
Explanation:
It is an open source electronics platform based on easy-to-use hardware and software. Arduino boards can read input and turn it into an output.
Question 60:
What is Neural Network?
Explanation:
Neural Network is a replication of the firing of neurons in our brain, which facilitates learning, although on a less complex scale.
Question 61:
What do you mean by Open-source Hardware?
Explanation:
- Open source hardware is similar to open source software.
- Ardunio is open source. The source code for which the Java environment is released under the GPL and C/C++ is under LGPL.
Question 62:
What is Raspberry Pi?
Explanation:
Raspberry Pi is a microcomputer that can be connected to a peripheral device. We can execute a number of tasks in a Raspberry Pi including, creating spreadsheets, coding, games etc.
Question 63:
How is Raspberry Pi used in IoT?
Explanation:
Raspberry Pi is a platform to develop many IoT based applications. IoT requires a network of devices and software to connect and exchange data. Raspberry Pi can provide this platform for it.
Question 64:
List any two real-life applications of Natural language processing.
Explanation:
- Google Translate
- Chat bots
- Siri, Alexa
Question 65:
What is Ethical Hacking?
Explanation:
Ethical Hacking is when a person is allowed to hack the system with the permission of the owner to find any bug in the system and to fix it.
Question 66:
What is the difference between IP and MAC address?
Explanation:
- IP Address – IP address is assigned to a device so that it can be located on the network.
- MAC Address – MAC Address is a unique serial number assigned to every network interface on every device.
Question 67:
Explain LAN
Explanation:
LAN or Local Area Network is used to connect devices such that they are able to share resources and exchange information. LAN is of two types, wireless LAN and wired LAN.
Question 68:
What is VPN?
Explanation:
VPN or Virtual Private Network is a private Wide Area Network built on the Internet. It allows the creation of a secured tunnel between different networks using the internet. VPN allows a client to connect to a network remotely.
Question 69:
What are Private and Special IP addresses?
Explanation:
- Private Address: These are specific IPs that are reserved specifically for private use only. These are non rout-able and cannot be used by the devices on the internet.
- Special Address: IP Range from 127.0.0.1 to 127.255.255.255 are network testing addresses also known as loop-back addresses. These are the special IP addresses.
Question 70:
What is DNS?
Explanation:
DNS is the Domain Name System. It basically translates the domain name of their corresponding IPs. It uses port 53 by default.
Question 71:
What is the main purpose of an OS? What are the different types of OS?
Explanation:
The function of an OS is to execute user programs and make it easier for the users to interact with the system. It is designed to ensure that the system performs better by managing all computational activities.
Types of OS:
- Batched OS (Example: Payroll System, Transactions Process, etc.
- Multi-Programmed OS (Example: Windows O/S, UNIX O/S, etc.)
- Timesharing OS (Example: Multics, etc.
- Distributed OS (LOCUS, etc.)
- Real-Time OS (PSOS, VRTX, etc.)
Question 72:
What is GUI?
Explanation:
GUI or Graphical User Interface is an interface that allows users to use graphics to interact with the OS. Its function is to make the OS more user friendly and less complex. Instead of having to memorize commands, users can just click on a button and execute the procedure.
Question 73:
What do you mean by RTOS?
Explanation:
Real Time Operating System of RTOS is a type of OS used for real time applications. It is used for tasks that are needed to be executed within a short period of time. It’s designed for applications where data processing should be done in a fixed and small measure of time.
Question 74:
Name some of the most famous OS.
Explanation:
- MS-Windows
- Ubuntu
- Mac OS
- Fedora
- Solaris
- Free BSD
- Chrome OS
- CentOS
- Debian
- Android
Question 75:
What is IPC?
Explanation:
IPC or Interprocess Communication is a mechanism that requires the use of resources like memory that is shared between processes or threads. With IPC, the OS allows different processes to communicate with each other. It is simply used for exchanging data between multiple threads in one or more programs or processes.
Deloitte most asked 30 questions
Question 1
Is FILE a built-in data type in C language?
Answer
No. File is a structure that is defined in stdio.h
Question 2
How can you print a (backslash) using any of the printf() family of functions?
Answer
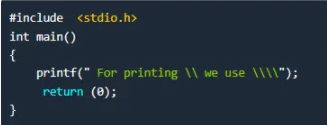
Question 3
What is nested structure in C?
Answer
Structure can be nested in 2 ways:
- By separate structure
- By embedded structure
Question 4
When is a function declared in C?
Answer
A function is declared when the function is defined in one source file and is called in another file.
The function is declared at the top of the file calling that function.
Question 5
What is the volatile keyword in JAVA?
Answer
Volatile keyword is used to modify the value of a variable by different threads.
Using this multiple threads can use a method and instance of the classes at the same time.
Question 6
What are the OOPS concepts used in JAVA?
Answer
Object-Oriented Programming or OOPs is a programming style that is associated with concepts like:
- Inheritance: Inheritance is a process where one class acquires the properties of another.
- Encapsulation: Encapsulation in Java is a mechanism of wrapping up the data and code together as a single unit.
- Abstraction: Abstraction is the methodology of hiding the implementation details from the user and only providing the functionality to the users.
- Polymorphism: Polymorphism is the ability of a variable, function or object to take multiple forms.
Question 7
How can you create threads in JAVA?
Answer
Threads are created in JAVA by implementing the runnable interface and overriding the run() method.
Question 8
What is a binary tree in JAVA?
Answer
Binary tree is a recursive data structure. In a binary tree every node can have a maximum of 2 children
Binary search tree is a common example of binary tree.
Question 9
What is an entity set?
Answer
Entity set is a set that contains the entities of same or similar types. An entity is an object which exists physically or conceptually.
It is of two types: Strong Entity Set and Weak Entity Set.
Question 10
What is heap memory?
Answer
Heap memory is a location in memory where memory is allocated in random access style. In a heap, memory is allocated and released in a random style not following a defined order.
Question 11
What are tokens in C++?
Answer
- Token is the smallest element of a C++ program that contains meaning for the compiler.
- Types of tokens include: Keywords, Identifiers, Strings etc.
- Tokens basically act as building blocks of a program.
Question 12
What are virtual functions in C++?
Answer
A virtual function is a member function which is declared within the base class and re-defined by a derived class. It is declared using the virtual keyword.
Virtual functions are created for the purpose of runtime polymorphism.
Question 13
What is the difference between ‘a’ and “a” in C++?
Answer
Question 14
What is an object relational database?
Answer
An object relational database(ORD) is a combination of relational database(RDBMS) and object oriented database (OODBMS).
Example: PostgreSQL and Oracle
Question 15
What is a cursor?
Answer
A cursor is defined as a temporary space created in memory when an SQL command is executed.
It is of two types: Implicit cursor and Explicit cursor.
- An Implicit cursor is automatically created when a statement is executed.
- An explicit cursor needs to be defined by the user. It can be defined by providing a name.
Question 16
What is a proxy server?
Answer
A proxy server functions as a bridge or relay between the client and server. The purpose of proxy server is to prevent cyber attacks and is a built-in tool in the firewall.
Question 17
What is a real time operating system?
Answer
Real time operating system (RTOS) is an operating system that serves real time applications, processing data as it comes in without any delay.
RTOS switches between tasks rapidly and gives the impression of multitasking.
Question 18
What is a friend function in C++?
Answer
A friend function is a function that can access private, protected and public members of a class. It is specified outside the class but can access all its members. It is declared using the friend keyword.
Question 19
What is an empty interface in java?
Answer
An empty interface does not contain any methods or fields. By implementing an empty interface a class exhibits special behavior with respect to the interface implemented.
An empty interface is also called a Marker Interface.
Question 20
What environment variables do I need to get on my machine to run JAVA?
Answer
The PATH and CLASSPATH, are the two environmental variables that should be present in a machine to compile and run JAVA.
Question 21
What is STL?
Answer
STL or Standard Template Library is a library consisting of classes, algorithms and iterators. It provides many of the basic data structures and algorithms.
The components of STL are in the form of templates. It is available in C++.
Question 22
Explain synchronization in respect to multithreading.
Answer
Synchronization is the capability to control the access of multiple threads to shared resources.
The main purpose of synchronization is to avoid any thread interference. Synchronization enables that at a time only one thread can access the resources.
Question 23
What is garbage collection in JAVA?
Answer
Garbage collection is the process to detect unused memory and recycle this memory for use. Garbage collection saves the user from manually deallocating memory.
Question 24
What is the lambda function in python?
Answer
Lambda function can be defined without a name. They are also called as the anonymous function.
These functions are defined using the lambda keyword. Lambda functions are used to reduce the length of code.
Question 25
What are OOPs concepts used in Python?
Answer
OOPS concepts used in Python are:- Class, Objects, Polymorphism, Encapsulation and Inheritance.
Question 26
What is docstring in Python?
Answer
Docstring or documentation strings is used for associating documentation with python modules, functions, classes and methods.
Doctrings are declared using the ‘’’triple single quotations’’’ or “””triple double quotations”””. Doctrings can be accessed using __doc__ method of the object.
Question 27
How to see object methods in Python?
Answer
Using the help() command.
Question 28
What are VTABLE and VPTR?
Answer
- VTABLE – virtual table. It is created during compilation for every single class. It contains the derived versions of virtual functions.
- VPTR – virtual pointer. It is a data member that the compiler inserts into the class specification and initializes to a virtual table from within the constructor.
Question 29
What is the Collection API?
Answer
Collection API provides a set of classes and interfaces that makes it easier to work with collections of objects such as lists, maps etc.
Question 30
How to solve ClassCastException?
Answer
ClassCastException is the child class of RuntimeException that arises while typecasting.
It can be solved by ensuring that while typecasting, the new type belongs to one of its parent classes. Also not to typecast a parent class onto its child class.
Deloitte coding questions
Question 1
Write a function that takes an array arr of size N-1 containing integers in the range [1, N] and returns the missing number from the sequence of the first N integers.
Question 2
Write a function that takes two sorted arrays, A and B, as well as the size of array A and the number of elements in array B. Array A has a sufficiently large buffer at the end to accommodate the elements of array B. The function should merge the two arrays in sorted order.
Example:
# Given arrays
a = [10, 12, 13, 14, 18, None, None, None, None, None]
b = [16, 17, 19, 20, 22]
size_of_a = 5 # Size of non-buffer part in array A
size_of_b = 5 # Size of array B
# Function call to merge arrays
merge_sorted_arrays(a, b, size_of_a, size_of_b)
# Output array after merging
# a = [10, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 22]
“`
Ensure that the function efficiently merges the two sorted arrays into array A, considering the provided buffer space.
Question 3
Write a function that takes an array `arr[]` of n integers and constructs a product array `prod[]` of the same size. Each element `prod[i]` should be equal to the product of all elements in `arr[]` except `arr[i]`. Solve the problem without using the division operator and with a time complexity of O(n).
Example:
# Given array
arr = [10, 3, 5, 6, 2]
# Function call to construct the product array
result = construct_product_array(arr)
# Output product array
# result = [180, 600, 360, 300, 900]
“`
Ensure that the function efficiently computes the product array without using division and with a linear time complexity.
Question 4
Design a snake and ladder game. Write a class or functions that simulate the gameplay, allowing players to roll dice and move through the board based on the outcome. Include the functionality to handle snakes and ladders, ensuring that the game state is updated accordingly
Question 5
Given an integer N, the task is to convert the given number into words.
Examples :
Input: N = 438237764
Output: Four Hundred Thirty Eight Million Two Hundred Thirty Seven Thousand Seven Hundred Sixty Four
Input: N = 1000
Output: One Thousand
Question 6
Write a function that takes the sum `S` and xor `X` of two numbers `a` and `b` as input and finds the numbers `a` and `b` such that they minimize the value of `X`.
Example:
# Given sum and xor
S = 17
X = 13
# Function call to find the numbers minimizing X
result_a, result_b = find_numbers_minimizing_X(S, X)
# Output
# result_a = 2
# result_b = 15
“`
Ensure that the function handles different input values and correctly identifies the numbers `a` and `b` that minimize the given xor `X`.
Question 7
Write a function that takes the sum X and xor Y of two numbers A and B as input and finds the numbers A and B such that they satisfy the given conditions:
X=A+B
Y=A⊕B
Question 8
Write a function that takes an integer array coins representing coins of different denominations and an integer amount representing a total amount of money. The function should return the fewest number of coins needed to make up that amount. If it’s not possible to make up the amount with the given coins, return -1.
Question 9
Write a function that takes the root of a binary tree containing digits from 0 to 9 only. Each root-to-leaf path in the tree represents a number, and the function should return the total sum of all root-to-leaf numbers.
Question 10
Write a function that takes an array of random numbers as input and pushes all the zeros to the end of the array. The function should modify the input array in-place, maintaining the order of all other elements. The expected time complexity is O(n), and the extra space used should be O(1).
Question 11
Write a function that takes an integer k and a queue of integers as input. The task is to reverse the order of the first k elements of the queue, leaving the other elements in the same relative order.
Question 12
Write a function that takes the root of a tree and an integer k as input and prints all the nodes that are at a distance of k from the root.
Question 13
Write a function that takes a linked list and an integer N as input and returns the value at the Nth node from the end of the linked list.
Question 14
Design a database schema for an Online Movie Booking Site. Define the necessary tables and relationships to store information about users, movies, theaters, showtimes, and bookings. Include primary keys, foreign keys, and relevant attributes for each table.
Question 15
Implement a method that takes the number of steps n as input and returns the count of possible ways a child can run up the staircase. The child can hop either 1 step, 2 steps, or 3 steps at a time.
Question 16
Implement a function that takes an array coins[] of size N representing different coin denominations and a target value V. The task is to find the minimum number of coins required to make the given value V. If it’s not possible to make the change, the function should return -1.
Question 17
Implement a function that takes two n-ary trees and their respective edges as input and checks if they are mirror images of each other. The number of edges is given by e, and two arrays A[] and B[] represent the edges. Each array has 2*e space-separated values u,v denoting an edge from u to v for both trees.
Question 18
Implement a function that takes arrival and departure times of trains as input and returns the minimum number of platforms required for the railway station so that no train is kept waiting. The arrival and departure times are given in two arrays, arrival[] and departure[].
Question 19
Implement a function that takes an array of size N containing only 0s, 1s, and 2s and sorts the array in ascending order. The sorting should be done in-place.
Question 20
Implement a function that takes two strings as input and checks whether the given strings are anagrams of each other or not.
Question 21
Implement a function that takes two non-negative integers num1 and num2 represented as strings and returns the product of num1 and num2, also represented as a string.
Question 22
Design a low-level system for an elevator. Consider the control system, hardware, safety measures, and user interfaces. Your goal is to create a comprehensive design that covers various aspects of elevator functionality.
Question 23
Write a function that takes a positive integer as input and returns its prime factorization. The prime factorization of a number is the list of prime numbers that multiply together to form the original number.
Question 24
Write a function that takes an array A representing the remembered roll results, the number of forgotten rolls F, and the desired arithmetic mean M. The function should return all possible results of the missing rolls in array format.
Question 25
Given a binary 2D matrix, find the number of islands. A group of connected 1s forms an island. For example, the below matrix contains 4 islands.
Example:
Input: mat[][] = {{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 0}}
Output: 4
Question 26
Given the arrival and departure times of all trains that reach a railway station, find the minimum number of platforms required for the railway station so that no train waits.
Question 27
You are given the arrival and departure times of trains that reach a railway station. Your task is to find the minimum number of platforms required for the railway station to ensure that no train waits.
Question 28
Given a string, find the count of distinct subsequences of it.
Question 29
Given a number N, The task is to find the length of the longest consecutive 1s series in its binary representation.
Question 30
You are given an array arr[] containing integers. Your task is to rearrange the elements of the array such that all non-zero elements are moved to the beginning of the array, and the remaining positions are filled with zeros.


